Laser Welding Machines: Advancements in Precision and Efficiency for Industrial Applications
Laser welding machines represent a significant leap forward in industrial technology, offering unparalleled precision, speed, and versatility in a variety of welding applications. Whether for automotive, aerospace, electronics, or other manufacturing sectors, laser welding has become a standard for high-quality welds in diverse industries. This article will explore the capabilities of laser welding machines, including portable models, the cost considerations involved, and the growing demand for laser welding solutions across various sectors.
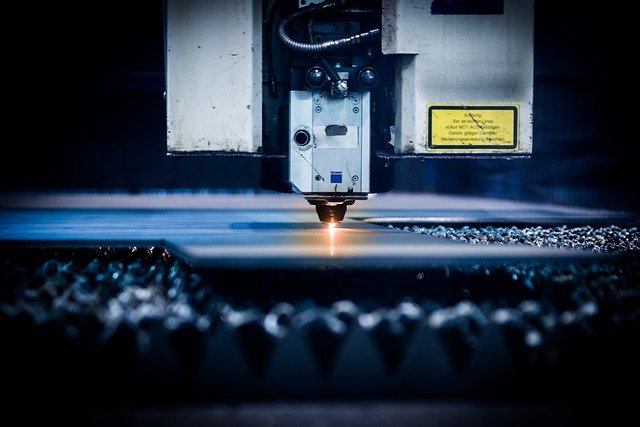

Laser welding machines represent one of the most significant technological advancements in modern manufacturing. These sophisticated systems harness the power of concentrated light energy to join materials with remarkable precision and efficiency. Unlike traditional welding methods that rely on electrical arcs or gas flames, laser welding uses a focused beam of light that generates intense heat at the exact point of application. This precision allows for exceptional control over the welding process, producing high-quality joints with minimal thermal distortion. As industries continue to demand higher quality standards and greater production efficiency, laser welding technology has evolved to meet these challenges across numerous applications.
How Laser Welders Transform Industrial Manufacturing
Laser welders have fundamentally changed manufacturing capabilities across multiple industries. The technology offers several distinct advantages over conventional welding methods. First, the concentrated energy delivery creates a narrow heat-affected zone, preserving the material properties surrounding the weld. This precision is particularly valuable when working with sensitive components or heat-vulnerable materials. Additionally, laser welders can achieve deep penetration welds with exceptional strength characteristics, often surpassing traditional welding methods in terms of joint integrity.
The automation potential of laser welding systems has also transformed production environments. Modern laser welders integrate seamlessly with robotic systems, enabling highly repeatable processes that maintain consistent quality across thousands of parts. This automation capability has proven especially valuable in industries like automotive manufacturing, aerospace, and electronics, where precision and reliability are paramount. The ability to program complex welding patterns and execute them with computer-controlled accuracy has elevated manufacturing standards while reducing the reliance on skilled manual welders.
Innovations in Laser Cutting Machine Technology
While primarily designed for joining materials, many laser systems incorporate cutting capabilities, making them versatile tools in manufacturing environments. Laser cutting machines utilize the same fundamental technology as laser welders but focus the beam energy to vaporize or melt material for precise cutting operations. These dual-function systems have become increasingly popular as manufacturers seek to consolidate equipment and streamline production processes.
Modern laser cutting machines feature advanced beam control technologies that enable exceptionally fine cuts with minimal kerf width (the width of material removed during cutting). This precision allows for intricate pattern cutting and minimal material waste. Additionally, the non-contact nature of laser cutting eliminates tool wear concerns associated with traditional cutting methods. Recent innovations in beam source technology have also expanded the range of materials that can be effectively processed, including highly reflective metals like copper and aluminum that were previously challenging for laser systems.
The integration of computer-aided design (CAD) and computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) software has further enhanced laser cutting capabilities. Manufacturers can now translate complex digital designs directly to the laser system, enabling rapid prototyping and production of sophisticated components without the need for physical tooling changes. This digital workflow has dramatically reduced setup times and increased manufacturing agility.
Advantages of Portable Laser Welding Machines
The development of portable laser welding machines represents a significant breakthrough in bringing advanced welding capabilities to diverse work environments. These compact systems offer remarkable flexibility compared to their stationary counterparts, allowing operators to perform precision welding operations in the field, at customer sites, or in areas of manufacturing facilities where fixed equipment cannot reach. The portability factor has opened new possibilities for maintenance operations, on-site repairs, and custom fabrication work.
Modern portable laser welders utilize fiber laser technology, which delivers high power output from relatively compact sources. These systems typically feature flexible delivery fibers that carry the laser beam from the source to a handheld welding head, giving operators significant freedom of movement. Advanced cooling systems and power management features enable these portable units to maintain stable performance despite their compact size. Many models also incorporate built-in shielding gas delivery systems to protect the weld area from atmospheric contamination.
The user-friendly nature of portable laser welding machines has expanded their adoption across industries. Intuitive interfaces, preset welding parameters for common materials, and real-time monitoring capabilities make these tools accessible to operators with varying levels of experience. This accessibility has been particularly valuable in addressing skilled labor shortages in the welding industry, as portable laser systems require less extensive training than traditional welding methods while producing consistent, high-quality results.
Understanding Portable Laser Welding Machine Price Factors
The cost of portable laser welding equipment varies significantly based on several key factors. Power output represents one of the most influential price determinants, with higher-powered systems commanding premium prices but offering greater versatility across material types and thicknesses. Beam quality—measured by parameters like beam parameter product (BPP) and M² value—also impacts pricing, as superior beam characteristics enable more precise welding capabilities. Additional features like programmable weld patterns, integrated vision systems, and advanced monitoring capabilities further influence the final cost.
| Portable Laser Welding Machine Type | Power Range | Typical Price Range (GBP) | Key Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Entry-Level Handheld | 300-600W | £25,000-£45,000 | Light repair work, thin sheet metal, jewelry |
| Mid-Range Portable | 600-1000W | £45,000-£85,000 | General fabrication, automotive repair, medium-thickness materials |
| Industrial Portable | 1000-2000W | £85,000-£150,000 | Heavy fabrication, thicker materials, high-volume production |
| Advanced Mobile System | 2000W+ | £150,000-£300,000+ | Specialized applications, exotic materials, integrated automation |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
Beyond the initial equipment investment, prospective buyers should consider total cost of ownership factors. Consumables like protective lenses, shielding gas, and replacement parts contribute to operational expenses. Power consumption varies between models, with more efficient systems offering long-term savings despite higher upfront costs. Maintenance requirements and service intervals also differ significantly between manufacturers and models. Most reputable suppliers offer service contracts that include regular preventive maintenance, which helps ensure optimal performance and longevity of the equipment.
Integration of Laser Welding in Modern Manufacturing
The integration of laser welding technology into broader manufacturing ecosystems represents a significant trend in industrial automation. Modern laser welding systems increasingly feature Industry 4.0 connectivity, allowing them to communicate with other production equipment, quality control systems, and enterprise resource planning software. This connectivity enables real-time process monitoring, adaptive control mechanisms, and comprehensive data collection for quality assurance and process optimization.
Manufacturers are leveraging these capabilities to implement closed-loop production systems where laser welding machines automatically adjust parameters based on incoming material variations or quality feedback. Vision systems integrated with laser welders can perform pre-weld inspections, real-time weld monitoring, and post-weld quality verification, ensuring consistent results even with material variations. The data generated through these connected systems provides valuable insights for continuous improvement initiatives and predictive maintenance programs.
As sustainability concerns grow across industries, the energy efficiency and precision of laser welding technology have become increasingly attractive. The focused energy delivery minimizes waste heat generation compared to traditional welding methods, reducing overall energy consumption. Additionally, the precision of laser welding processes minimizes material waste through reduced rework rates and optimized joint designs. These sustainability benefits, combined with the productivity advantages of laser technology, continue to drive adoption across diverse manufacturing sectors.
Laser welding machines have transformed industrial manufacturing through unparalleled precision, efficiency, and versatility. From stationary high-powered systems to increasingly sophisticated portable units, these technologies continue to evolve to meet demanding production requirements. As costs gradually decrease and capabilities expand, laser welding is becoming accessible to a broader range of manufacturers. The ongoing integration of these systems with digital manufacturing platforms and automation technologies suggests that laser welding will remain at the forefront of industrial joining processes, enabling new possibilities in product design and manufacturing efficiency.