Understanding Portable Laser Welders: Safety, Efficiency, and Cost Considerations
Portable laser welders are becoming an increasingly practical option for small workshops, repair technicians, and manufacturers who need precise, clean welds without the footprint of a full industrial machine. While these compact systems can offer faster processing, reduced cleanup, and greater flexibility, they also come with important safety requirements and cost factors that buyers should understand. This guide takes a realistic look at how portable laser welders work, what benefits they provide, what limitations they still have, and what you should consider before investing in one.
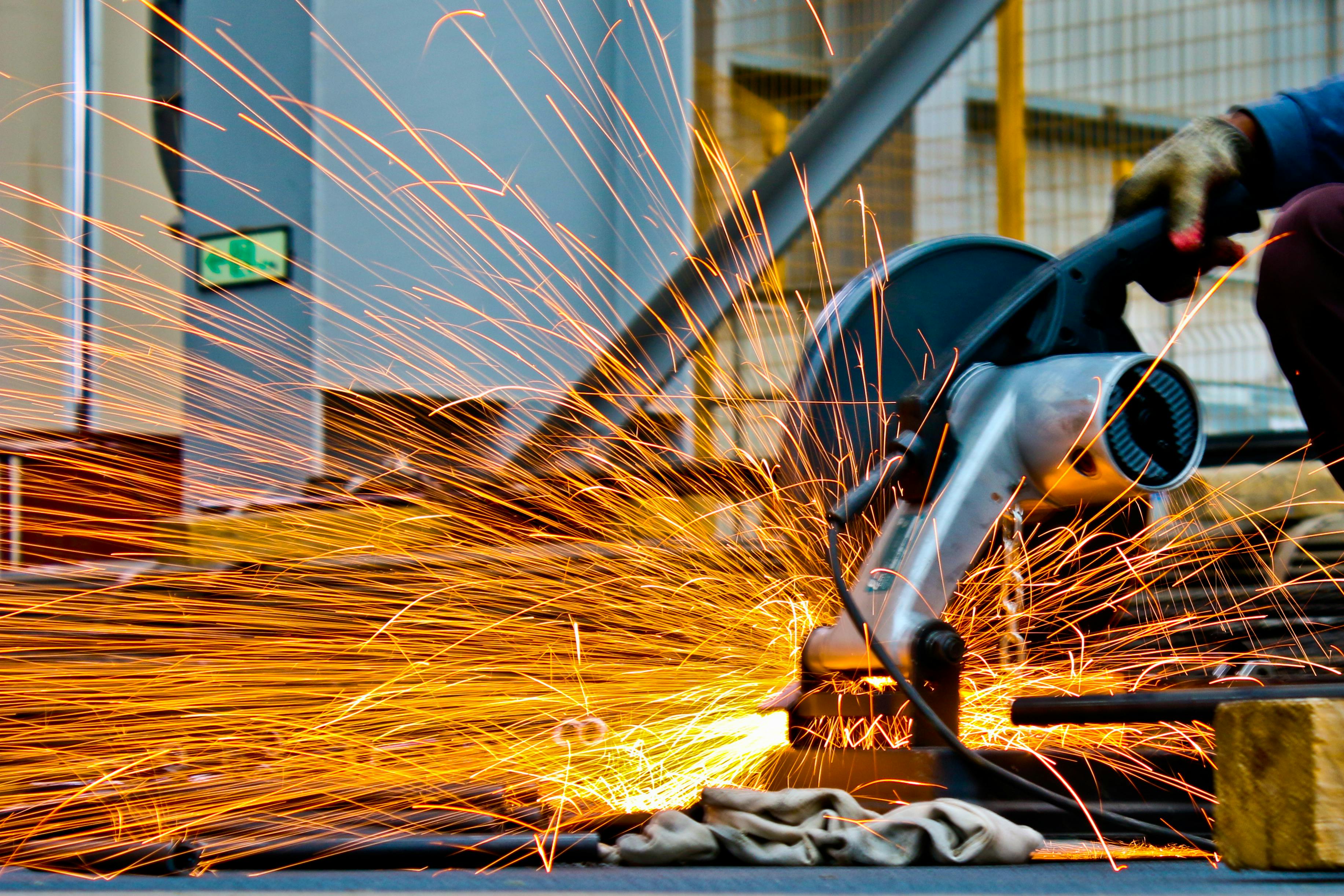

Portable laser welding technology has revolutionized how professionals approach precision joining tasks. Unlike conventional welding methods that rely on consumable electrodes or gas flames, these systems use concentrated laser energy to create clean, precise welds with minimal heat-affected zones. This technology enables welders to work on delicate materials and achieve results that would be challenging or impossible with traditional equipment.
What Makes Portable Laser Welder Technology Unique
A portable laser welder operates by focusing a high-intensity laser beam onto the workpiece surface, creating localized heating that melts and fuses materials together. The precision of this process allows for welding thicknesses ranging from thin foils to several millimeters of metal, depending on the laser power output. Most handheld systems feature fiber laser technology, which provides excellent beam quality and energy efficiency compared to older CO2 laser systems.
The portability aspect comes from integrated cooling systems, compact power supplies, and ergonomic handpiece designs that allow operators to move freely around workpieces. This mobility is particularly valuable in field repairs, large assembly operations, and situations where bringing the work to a stationary welding station is impractical.
Safety Protocols for Handheld Laser Welding Machine Operation
Operating any laser welding system requires strict adherence to safety protocols due to the intense laser radiation involved. Operators must wear appropriate laser safety eyewear rated for the specific wavelength being used, typically around 1070 nanometers for fiber lasers. The welding area should be properly enclosed or marked to prevent accidental exposure to laser radiation.
Ventilation systems are crucial when using portable laser welding systems, as the welding process can produce metal fumes and vapors that pose respiratory hazards. Many modern units include integrated fume extraction systems, but additional ventilation may be necessary in enclosed spaces. Regular safety training and equipment maintenance ensure safe operation and compliance with occupational safety standards.
Applications and Efficiency Benefits of Industrial Laser Welder Systems
Industrial laser welder applications span numerous sectors, from aerospace component repair to medical device manufacturing. The precision and speed of laser welding make it ideal for high-value applications where weld quality directly impacts product performance. Automotive manufacturers use these systems for battery pack assembly, while jewelry makers appreciate the ability to weld near heat-sensitive components without damage.
Efficiency gains come from reduced setup times, minimal post-weld finishing requirements, and the ability to weld dissimilar materials that traditional methods cannot join effectively. The concentrated heat input reduces distortion and eliminates the need for filler materials in many applications, resulting in stronger, cleaner joints.
Comparing Portable Laser Welding System Features
When evaluating different portable laser welding systems, key specifications include laser power output, pulse duration control, beam quality, and cooling system efficiency. Higher power units typically range from 1000 to 2000 watts, suitable for thicker materials and faster welding speeds. Lower power systems, around 500 to 1000 watts, offer excellent precision for thin materials and detailed work.
User interface design varies significantly between manufacturers, with some offering touchscreen controls and preset welding programs, while others focus on simplified manual controls. Weight and ergonomics of the handpiece become important factors during extended use, as operator fatigue can affect weld quality and safety.
| System Type | Power Range | Typical Cost | Key Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Entry-Level Portable | 500-1000W | $15,000-$35,000 | Jewelry, electronics, thin metals |
| Mid-Range Handheld | 1000-1500W | $35,000-$65,000 | Automotive, general fabrication |
| Industrial Systems | 1500-2000W+ | $65,000-$120,000+ | Aerospace, heavy manufacturing |
| Specialized Units | Variable | $25,000-$80,000 | Medical devices, precision repair |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
Investment Considerations for Laser Welding Machine for Sale Options
When searching for a laser welding machine for sale, total cost of ownership extends beyond the initial purchase price. Maintenance requirements, consumable costs, and training expenses should factor into the investment analysis. Most systems require periodic maintenance of optical components, cooling system servicing, and calibration checks to maintain optimal performance.
Financing options are often available through equipment manufacturers or leasing companies, making these systems accessible to smaller operations that cannot make large capital investments. Some suppliers offer demonstration programs or trial periods that allow potential buyers to evaluate system performance with their specific applications before committing to purchase.
Warranty coverage varies significantly between manufacturers, with some offering comprehensive service packages while others provide basic component warranties. Consider the availability of local service support, as laser systems require specialized technical expertise for repairs and maintenance.
Future Developments in Portable Laser Welding Technology
Continuing developments in laser technology promise even more capable and user-friendly portable welding systems. Improvements in laser diode efficiency are reducing power consumption and heat generation, enabling longer operating periods and smaller cooling systems. Advanced beam shaping technologies are expanding the range of materials and joint configurations that can be effectively welded.
Integration with digital systems is enabling real-time weld monitoring, quality control, and data logging capabilities that support Industry 4.0 manufacturing initiatives. These features help operators maintain consistent quality while providing documentation for quality assurance and traceability requirements.
Portable laser welders represent a significant technological advancement that offers precision, efficiency, and versatility for a wide range of welding applications. Understanding the safety requirements, evaluating system features against specific needs, and considering total ownership costs enables informed decision-making when investing in this technology. As the technology continues to evolve, these systems will likely become even more accessible and capable, further expanding their adoption across industries.