What are the treatments for hair loss
Thinning hair and hair loss are common concerns that affect people of all ages, prompting many to seek effective treatment solutions. From mild hair thinning to more severe hair loss conditions, understanding the diverse therapeutic options available is crucial for addressing these issues and restoring hair health. This article explores the key treatments tailored to both thinning hair and hair loss, providing practical insights for those navigating these challenges.
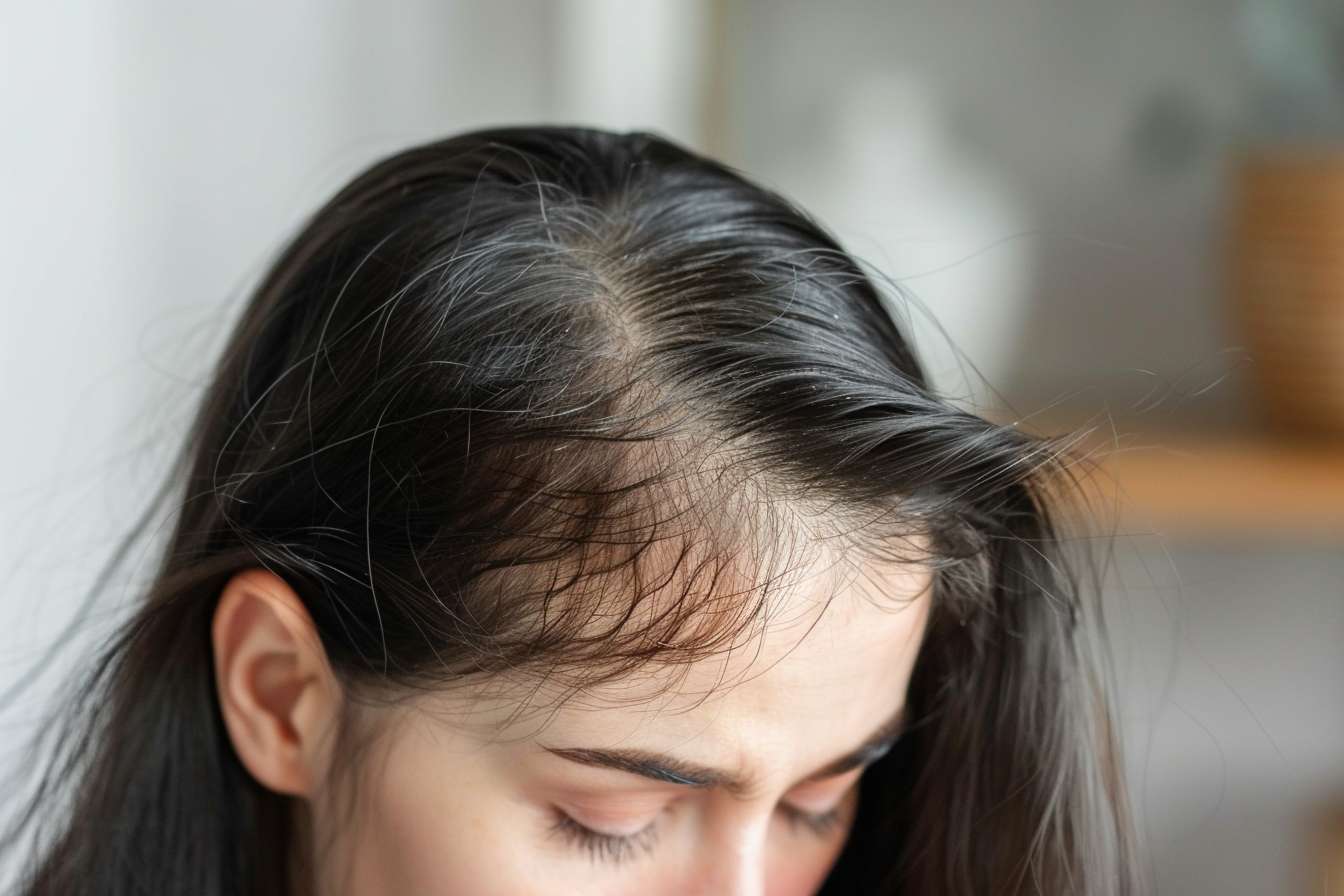

Understanding the available treatments for hair loss begins with recognizing that no single solution works for everyone. The effectiveness of any treatment depends on the underlying cause, the extent of hair loss, and individual health factors. Consulting a healthcare professional or dermatologist is essential to determine the most appropriate approach for your specific situation.
Medical Treatments for Thinning Hair and Hair Loss
Medical interventions remain among the most researched and widely used options for addressing hair loss. Two FDA-approved medications dominate this category: minoxidil and finasteride. Minoxidil, available over the counter as a topical solution or foam, works by stimulating hair follicles and prolonging the growth phase of hair. It is suitable for both men and women and typically requires consistent application for several months before results become visible. Finasteride, available by prescription, is an oral medication primarily used by men to treat male pattern baldness by blocking the hormone responsible for hair follicle shrinkage. Women who are pregnant or planning to become pregnant should not use finasteride due to potential risks. Other medical treatments include corticosteroid injections for alopecia areata, platelet-rich plasma therapy that uses concentrated blood components to stimulate growth, and low-level laser therapy devices approved for home use. These treatments vary in cost, effectiveness, and accessibility, making professional guidance crucial.
Non-Medical Interventions for Hair Thinning and Loss
Beyond pharmaceuticals, several non-medical interventions offer alternatives or complementary approaches to managing hair loss. Hair transplant surgery represents a permanent solution for those with sufficient donor hair, involving the relocation of hair follicles from one area of the scalp to another. This procedure has advanced significantly with techniques like follicular unit extraction, which minimizes scarring and recovery time. Scalp micropigmentation provides a cosmetic solution by tattooing tiny dots on the scalp to create the appearance of fuller hair or a shaved head look. Wigs, hairpieces, and hair extensions offer immediate aesthetic improvements without medical intervention. Essential oils such as rosemary, peppermint, and lavender have gained attention for their potential to improve scalp health and stimulate hair growth, though scientific evidence remains limited compared to medical treatments. Scalp massage and microneedling are emerging as accessible methods that may enhance blood circulation and promote follicle health. While these interventions lack the rigorous clinical validation of medical treatments, many individuals report positive outcomes when used consistently.
Lifestyle Adjustments to Complement Hair Loss Treatments
Lifestyle factors play a significant role in hair health and can enhance the effectiveness of other treatments. Nutritional deficiencies, particularly in iron, zinc, biotin, and protein, can contribute to hair thinning. A balanced diet rich in vegetables, fruits, lean proteins, and healthy fats supports overall hair health. Stress management is equally important, as chronic stress can trigger or worsen conditions like telogen effluvium, where hair prematurely enters the shedding phase. Techniques such as meditation, regular exercise, and adequate sleep help reduce stress levels and promote hormonal balance. Avoiding harsh hair treatments, excessive heat styling, and tight hairstyles that pull on the scalp can prevent further damage to fragile hair. Gentle hair care practices, including using sulfate-free shampoos and minimizing chemical treatments, protect existing hair while creating an environment conducive to regrowth. Smoking cessation and limiting alcohol consumption also benefit hair health by improving circulation and nutrient delivery to hair follicles. These lifestyle adjustments do not replace medical treatments but serve as valuable complements that optimize conditions for hair retention and growth.
Combining Approaches for Better Results
Many individuals achieve the best outcomes by combining multiple treatment strategies. For example, using minoxidil alongside lifestyle modifications and stress reduction techniques may yield more noticeable improvements than any single method alone. Similarly, those undergoing hair transplant surgery often continue medical treatments to preserve remaining hair and support transplanted follicles. The key is consistency and patience, as most hair loss treatments require several months of regular use before visible results appear. Tracking progress through photographs and maintaining realistic expectations helps individuals stay motivated throughout the treatment process. Regular follow-ups with healthcare providers ensure that treatments remain appropriate and adjustments can be made as needed.
Understanding Treatment Limitations and Expectations
While numerous treatments exist, it is important to recognize their limitations. No treatment can completely reverse advanced hair loss or restore hair to its original density in all cases. Some forms of hair loss, such as scarring alopecia, may not respond to conventional treatments because hair follicles have been permanently damaged. Additionally, treatment effectiveness varies widely among individuals due to genetic factors, the underlying cause of hair loss, and how early intervention begins. Discontinuing certain treatments like minoxidil or finasteride often results in the gradual return of hair loss, meaning long-term commitment is necessary to maintain results. Understanding these realities helps individuals make informed decisions and avoid disappointment from unrealistic promises made by unverified products or services.
This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Please consult a qualified healthcare professional for personalized guidance and treatment.
Addressing hair loss requires a comprehensive approach that considers medical treatments, non-medical interventions, and lifestyle modifications. By understanding the available options and working closely with healthcare professionals, individuals can develop personalized strategies that address their specific needs and improve their chances of maintaining or regrowing hair. While no single solution guarantees success for everyone, the expanding range of evidence-based treatments offers hope and practical pathways for managing this common concern.